Oncologic Outcomes of ABO Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jee Youn Lee1, Deok Gie Kim1, Jae Geun Lee1, Juhan Lee1, Yoon Bin Jung1, Soo Jin Kim1, Man Ki Ju1, Sung Hoon Kim2, Myoung Soo Kim1, Soon Il Kim1, Dong Jun Joo1.
1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea; 2Department of Surgery, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
Introduction: ABO incompatible living donor liver transplantation (ABOi LDLT) could be one of the treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to overcome organ scarcity. However, desensitization protocol including B cell depletion besides traditional T cell suppression could be a risk factor for HCC recurrence that is a major cause of graft failure and patient death. There is no enough data of ABOi LT for HCC patients. Herein, we analyzed oncologic outcomes of ABOi LDLT comparing to ABO compatible LDLT.
Method: The data of 101 recipients who underwent LDLT for HCC were prospectively collected and reviewed. Of the patients, 21 patients underwent ABOi LT. We compared the pre- and post-transplant tumor factors, HCC recurrence and survival between ABOi and ABOc LT.
Result: There was no significant difference in pre-transplant tumor staging, recipient and donor demographics between the groups. One and 3-year recurrence-free survival rates were 89.8% and 86.9% for the ABOc LT group and 85.4% and 80.1% for the ABOi LT, respectively (P=0.439). One and 3-year overall survival rates were 96.3% and 88.1% for the ABOc LT group and 90.5% and 85.2% for the ABOi LT, respectively (P=0.651). In multivariate analysis, a pre-transplant AFP level over 400 ng/mL and a poorly differentiated HCC were the independent risk factor for HCC recurrence. A pre-transplant AFP level over 400 ng/mL were related to poor patient survival.
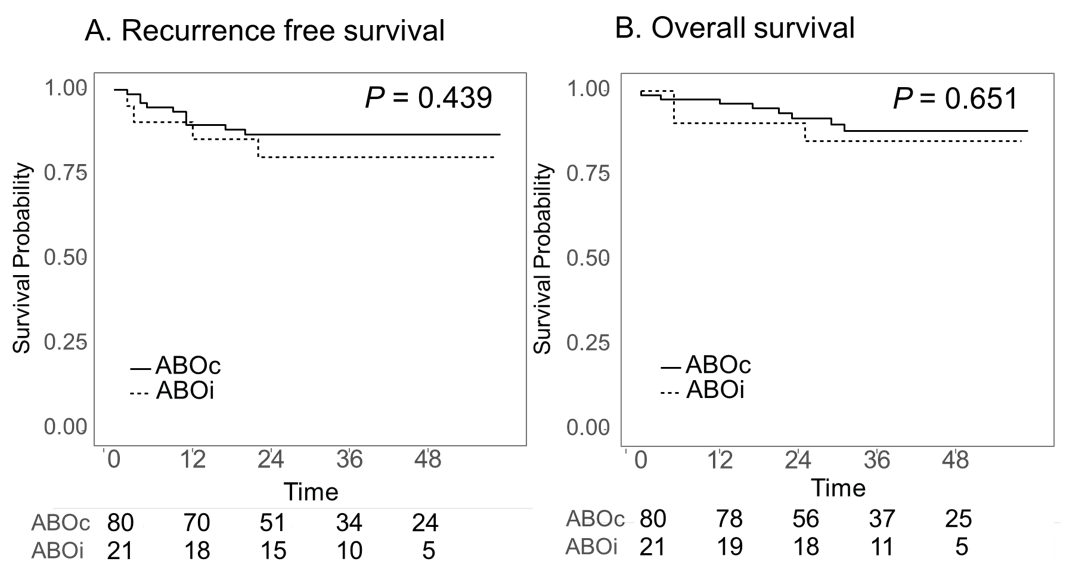
Conclusion: The HCC recurrence survival and overall survival of ABOi LT were comparable to those of ABOc LT. ABOi LT is safe and feasible option for HCC patients.
