A Signature of Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood that Enables Earlier Detection of Acute Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients.
Maria Hernandez-Fuentes1,3,8, Sofia Christakoudi1,2, Manohursingh Runglall 3, Paula Mobillo1, Tjir-Li Tsui1,3, Yogesh Karma3, Florence Delaney3, Rosa Montero3,4, Anastasia Spiridou 3, Sui Phin-Kon5, Beatriz Tucker5, Christopher Farmer6, Terry Strom 7, Steven Sacks 1, Graham Lord 1,3, Irene Rebollo-Mesa 1,2,8, Daniel Stahl 2, Paramit Chowdhury4.
1MRC Centre for Transplantation, King's College London, London , United Kingdom; 2Biostatistics and Health Informatics Department, Institute of Psychiatry Psychology and Neuroscience, King's College London, London, United Kingdom; 3NIHR Comprehensive Biomedical Research Centre , London, United Kingdom; 4Renal Unit, Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom; 5Renal Unit, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom; 6Renal Unit, East Kent Hospitals University NHS Foundation Trust, Canterbury, United Kingdom; 7Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard University, Boston, MA, United States; 8Global Exploratory Development, UCB Celltech, Slough, United Kingdom
KALIBRE (Kidney Allograft Immune Biomarkers of Rejection Episodes).
Background: Acute rejection (AR) is often indicated by an increase in creatinine levels, after a considerable graft damage has already occurred. There is, therefore, a need for early identification of AR. Monitoring of RNA gene signatures in peripheral blood and urine samples offers the opportunity for surveillance of the recipient immune system and earlier detection of acute rejection.
Samples: We examined RT-qPCR expression of 22 literature-based candidate genes in 335 longitudinal whole-blood samples from 27 stable kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) from the KALIBRE study (Kidney Allograft Immune Biomarkers of Rejection Episodes) and 237 samples from 27 KTRs with a biopsy-proven cellular rejection during the first post-transplant year. Creatinine in stable KTRs reached no higher than 20% above the reference range and had less than 15% standard deviation.
Methods: To account for post-transplantation changes unrelated to rejection, we generated time-adjusted gene expression as the residuals of linear mixed-effects models with stable patients. To select a parsimonious AR signature, we used penalised logistic regression with a pre-biopsy sample in rejectors and the median gene expression for each stable patient. As a test set we used the longitudinal data. We were also able to examine longitudinal expression of genes as well as effect of different anti-rejection therapies. We subsequently tested the performance of our signature in a second cohort.
Results: A 7-gene signature of AR showed area under the curve (AUC) 0.95 (95% confidence interval 0.91-1.00), sensitivity 0.85, specificity 0.93, positive and negative predictive values 0.92 and 0.86 and cross-validated AUC 0.85 (0.75-0.95). The estimated probability of rejection increased as early as six weeks prior to the AR biopsy and decreased after administration of treatment. Notably, gene expression in stable KTRs, as well as in rejectors, showed a pronounced variability, with 22% AR-positives longitudinal samples.
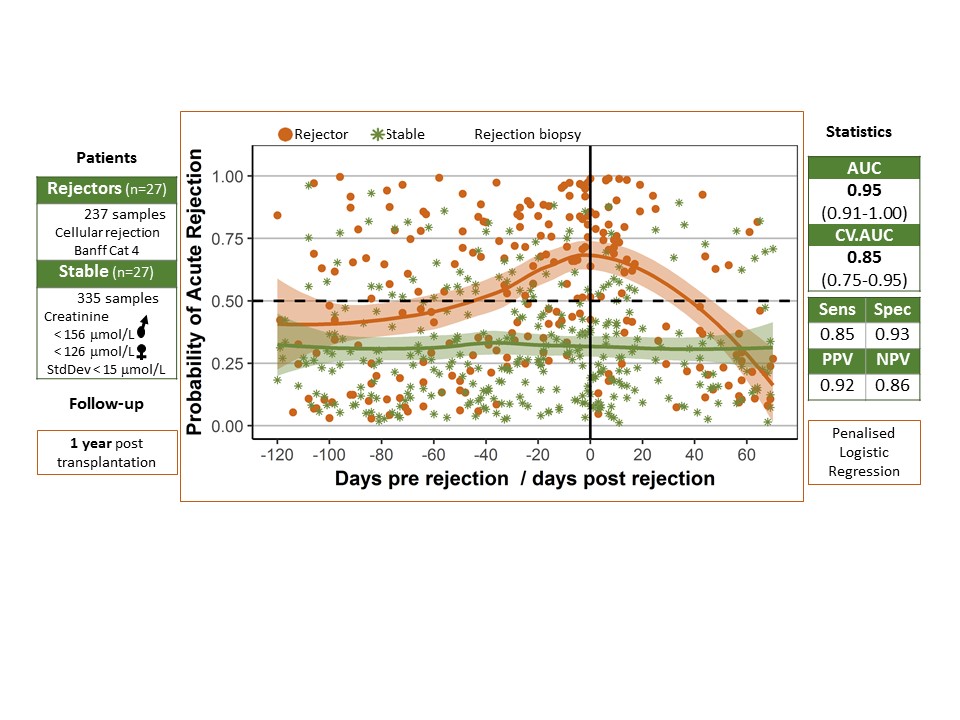
Conclusion: Molecular marker alterations in blood emerge well ahead of the time of clinically overt AR. Monitoring of a gene-expression signature of AR in peripheral blood could unravel AR-related pro-inflammatory activity and provide information on subclinical processes and further justification for a biopsy in cases of sustained kidney dysfunction with no marked change in creatinine.
Medical Research Council (MRC) (grants G0801537/ID: 88245 and MRC Centre for Transplantation, – MRC grant no. MR/J006742/1). MHF - HEALTH-F5– 2010–260687: The ONE Study. . SC, PM and MPH-F received funding from FP7-HEALTH-2012-INNOVATION-1 project number 305147: BIO-DrIM. . National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre at Guy’s and St Thomas’ and King’s College London.. NIHR Health Informatics Collaborative.
