The Efficacy of CMV Specific Immune Reconstitution is Highly Dependent on Donor/Recipient Serostatus and Type of Solid Organ Transplanted
Alda Saldan1, Carlo Mengoli1, Dino Sgarabotto1, Marianna Alessi4, Antonio Gambino3, Luciana Bonfante4, Patrizia Burra6, Francesco Marchini4, Barbara Rossi4, Patrizia Boccagni6, Anna Pompea Fraiese3, Giuseppe Toscano3, Silvano Fasolato5, Cristina Silvestre6, Francesco Paolo Russo6, Paolo Angeli5, Lucrezia Furian6, Monica Loy2, Giacomo Sturniolo6, Umberto Cillo6, Gino Gerosa2, Paolo Rigotti6, Federico Rea2, Giorgio Palù1, Davide Abate1.
1Department of Molecular Medicine, University of Padova, Padova, Italy; 2Department of cardiac surgery, chest and vascular sciences, University of Padova, Padova, Italy; 3 Cardiothoracic surgery unit, Padova General Hospital, Padova, Italy; 4Nephrology unit, Padova General Hospital, Padova, Italy; 5Department of Medicine, University of Padova, Padova, Italy; 6Department of surgery, oncology, gastroenterology, University of Padova, Padova, Italy
Introduction: The CMV specific immune recovery is known to control viral infection and disease. The CMV specific cell-mediated immunity (CMI) and CMV specific humoral immune response (IgG titer and IgG avidity) was explored as candidate biomarker predictive of CMV infection.
Materials: 653 observations from 297 SOT including 103 kidney (K), 60 liver (L), 47 heart (H), 87 Lung (Lu) transplants. The follow-up was 0-400 days after transplant. The following parameters were examined: 1) CMV serostatus before transplant 2) CMV IgG titer 3) CMV IgG avidity 4) CMV-ELISPOT 5) primary (D+/R-) or non-primary (D±/R+) CMV infection 6) CMV viremia. Data were statistically analyzed using ANOVA and linear regression analysis and spline model.
Results: The main findings of the study are: 1) CMV IgG titers and avidity are not predictive biomarker for CMV infection. The CMV IgG titer and IgG avidity levels are comparable either in infected and non-infected patients. 2) CMV viral load is statistically different between infected D±/R+ and D+/R-. The viral load in infected D+/R- is 1 Log higher compared to D±/R+ (10^5 vs 10^4 respectively) 4) The CMV immune reconstitution is more rapid and efficient in D±/R+ compared to D+/R- 5) D±/R+ and D+/R- Kidney and Lung transplants display a statistically significant lower CMI compared to heart and liver transplants; 6) Kidney and Lung transplants display a similar pattern of immune recovery 7) The CMV cell mediated immunity biomarker is predictive of infection in all organs with exception of lung transplants.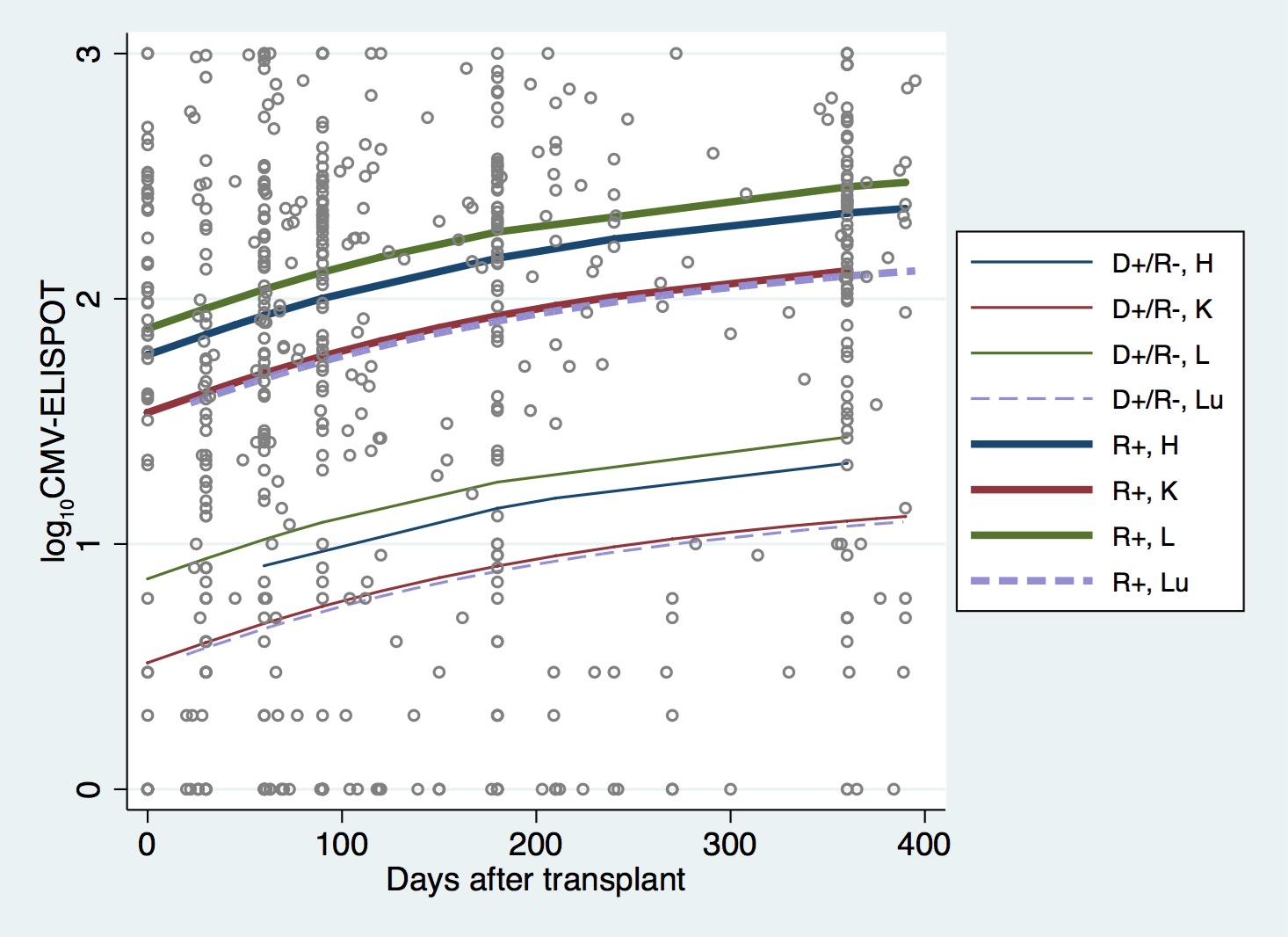
Conclusion: The study shows a marginal role of humoral immunity in controlling CMV infection. The pattern of CMI immune recovery is highly dependent upon pre-transplant CMV serostatus, type of organ transplant and immunosuppression therapy. High levels of CMV specific cell-mediated immunity correlate with a reduced CMV infection risk in heart, kidney and liver transplants. A different scenario emerged in lung transplants: high levels of circulating CMV specific T-cells can be found in lung transplants but cannot prevent CMV infection and clear the virus. In this view the lung may be considered a "sanctuary site" for CMV replication.
