Durable Macrochimerism (>8 weeks) and Pig-Specific T and B Cell Unresponsiveness Following hCD47+ Transgenic GalTKO Pig Intra-Bone Bone Marrow Transplantation in Baboons
Hironosuke Watanabe1, Shunichiro Nomura1, Yuichi Ariyoshi1, Thomas Pomposelli1, Lennan K Boyd1, Masayuki Tasaki1, Dilrukshi K Ekanayake-Alper1, Harrison C Glor1, Scott Arn1, Robert J Hawley1, Megan Sykes1, David H Sachs 1, Kazuhiko Yamada1.
1CCTI/Surgery, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, United States
Background: Recent data have suggested that low levels of preformed anti-non-Gal natural antibody (nAb) limit xenograft survival. Durable mixed xenogeneic chimerism resulted in tolerance of human T cell-independent B cells that produce xenoantibodies, including anti-non-Gal nAb, in mouse models. However, previous attempts at intravenous (IV) α-1,3-galactocyltransferase knockout (GalTKO) pig bone marrow (BM) transplantation (Tx) into non-human primates have been associated with very short-lived chimerism (<24 hours in most cases). In order to achieve improved engraftment with more persistent chimerism, we have recently developed an intra-bone BM (IBBM) Tx strategy in a pig-to-baboon model. We have reported continuous peripheral blood macrochimerism for up to 13 days (mean 7.7 days; range 3–13) post-IBBM/BM-Tx (n=6) and in three animals, macrochimerism reappeared at days 10, 14 and 21 (Am J Transplant 2015). Recent data has suggested that incompatibility between CD47 and SIRPα causes phagocytosis of porcine cells. In this study, we examined whether the use of BM cells from human CD47 (hCD47) transgenic pigs further improves durable chimerism and assessed anti-pig antibody responses following BM Tx,Methods: Four baboons received GalTKO/human CD47(hCD47)/hCD55 pig BM cells, and one received GalTKO/hCD55 porcine BM cells with a conditioning regimen consisting of whole body irradiation thymic, irradiation, ATG, and Rituximab followed by anti-CD40L antibody and MMF. Approximately 2/3 of BM cells were infused intraosseously and the remainder intravenously. Macrochimerism, anti-pig T cells responses, and anti-pig antibody responses were assessed following IBBM Tx. Results were compared with those from baboons that received GalTKO porcine BM cells without any other gene modification (n=6).
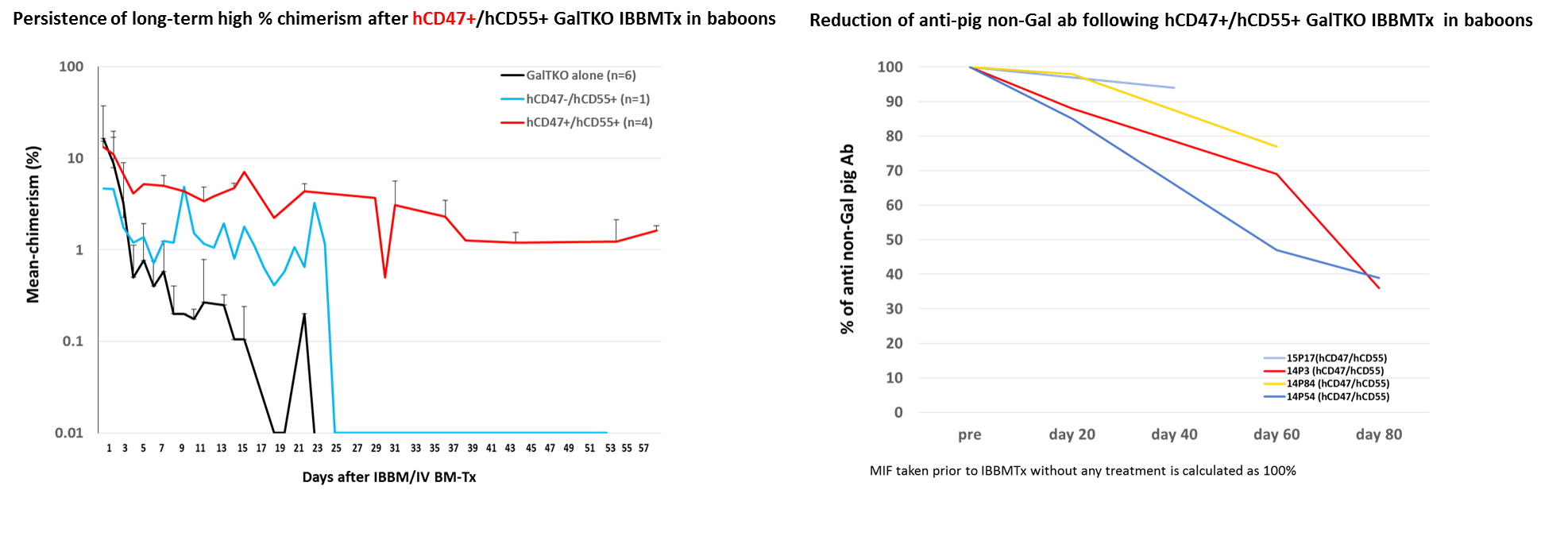
Results: As shown in the Figure (left panel), all four baboons that received hCD47+/hCD55+ porcine BM using the IBBM Tx method maintained durable macrochimerism for >50 days, and two of the 4 maintained blood levels above 1.6%, even at 8 weeks following IBBMTx (red line in the left panel of Fig). We also confirmed macrochimerism in recipients’ BM. A baboon that received hCD55+ but hCD47-negative porcine BM cells also had a slightly higher % of chimerism than GalTKO alone porcine BM cells in the first 3 weeks, but the duration was similar to GalTKO alone porcine BM cells (Blue line vs black line in the left panel of Fig). All recipients of IBBM Tx lost their anti-pig T cell responses in vitro and showed no development of elicited anti-pig ab. Notably, anti-pig nonGal nAb levels in three of 4 recipients of hCD47+/hCD55+ porcine BM cells declined markedly following IBBM Tx (right panel of Fig).
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of (1) durable macrochimerism beyond 8 weeks and (2) reduction of anti-non Gal nAb levels following hCD47+/hCD55+ GalTKO porcine IBBMTx in preclinical pig-to-non-human primate models. The results suggest that IBBMTx using hCD47+ porcine BM is a potent strategy to induce pig-specific T and B cell tolerance across xenogeneic barriers.
NIH P01AI45897 .
