The Mark of Zorro: IL35-coated Exosomes Cross-Dress and Exhaust Recipient T & B Cells During Transplant Tolerance
William Burlingham1, Jeremy A Sullivan1, Diego A Lema1, Yusuke Tomita2, Ying Zhou1, Dario Vignali3.
1Surgery, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, United States; 2Surgery, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan; 3Immunology, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, United States
In Spanish colonial California, the folk-hero "Zorro" left his mark on by a sword- slashed "Z" . In transplant recipients, rare Tregs also leave a mark on their conventional T & B LC targets. This mark is caused by Ag-specific CD4 Tregs that release IL35-coated exosomes, “cross-dressing” (xD) their targets with IL35.
Hypothesis: We wished to test 3 hypotheses related to this finding: 1) just as MHC+ exosome release by “passenger” DC greatly amplifies alloactivation by xD of host DC, IL35 suppression by passenger Tregs is greatly amplified by xD of host T cells; 2) monitoring circulating CD4+ T cells displaying IL35/xD-phenotype after heterotopic heart transplantation will correlate with biD regulation(HvG and GvH), and 3) that IL-35-induced “exhaustion” is a direct result of the IL35/xD-phenotype.
Approach: To this end we fully tolerized B6 “donor” mice with CBA DST + 125 ug (x3) MR1(anti-CD40L). In addition, we sub-optimally tolerized recipient CBA mice with B6 DST + 62.5 ug(x3) injections of MR1. On d.35 , the CBA mice received either a normal B6 heart allograft(uni-directional regulation) or one from a CBA-tolerized B6 donor(biD regulation).
Results: While the suboptimally tolerized CBA showed prolonged allograft survival, by 4 weeks all grafts were rejected(Fig 1).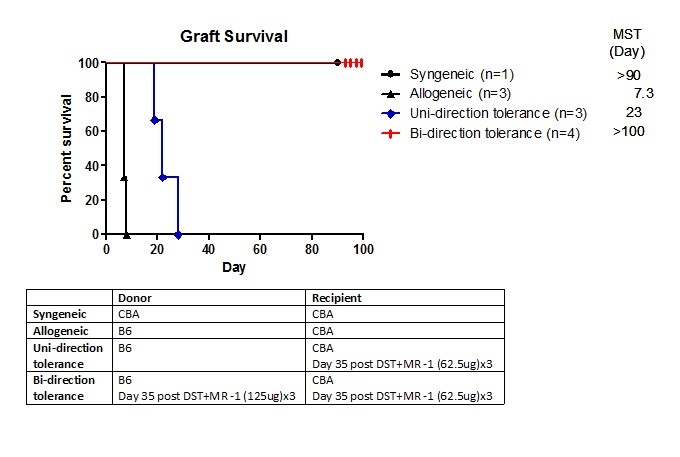 In contrast, when the heart from a fully-tolerized B6 mouse was transplanted (BiD regulation setting) in the same recipient, all grafts survived long term. We tested by flow cytometry the % of IL35/xD among conventional CD4 T cells circulating in peripheral blood (Fig 2).
In contrast, when the heart from a fully-tolerized B6 mouse was transplanted (BiD regulation setting) in the same recipient, all grafts survived long term. We tested by flow cytometry the % of IL35/xD among conventional CD4 T cells circulating in peripheral blood (Fig 2).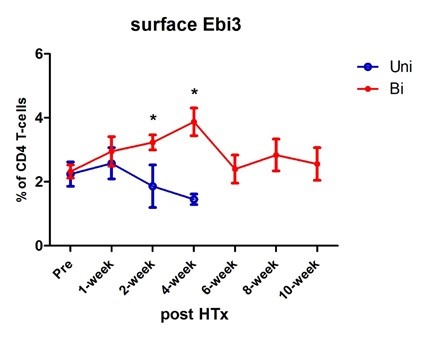 There was an initial slight increase, then the % began to drop at 2 wks and was lower than the starting level at the time of graft rejection (4 wk). In contrast, the PBMC-CD4 T cell % of IL35-xD cells continued to climb at 2 & 4 wks in the biD regulation group, after which the level stabilized at pre-Tx levels, suggesting an amplified impact of IL35 exosome production from the donor side. Figure 3
There was an initial slight increase, then the % began to drop at 2 wks and was lower than the starting level at the time of graft rejection (4 wk). In contrast, the PBMC-CD4 T cell % of IL35-xD cells continued to climb at 2 & 4 wks in the biD regulation group, after which the level stabilized at pre-Tx levels, suggesting an amplified impact of IL35 exosome production from the donor side. Figure 3 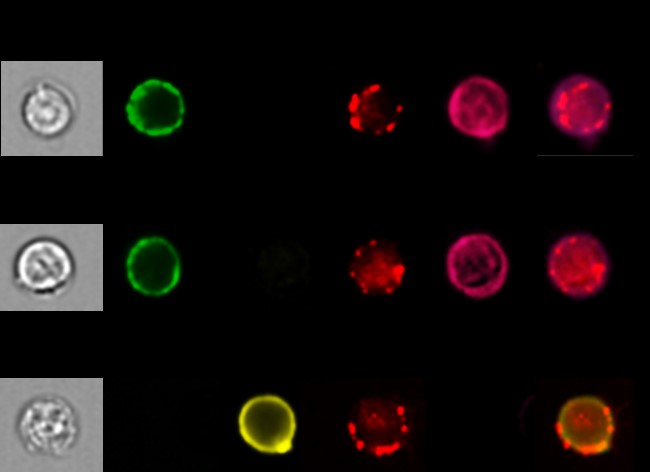 shows images from population microscopy, depicting the appearance of IL35-xD cells. The punctate surface staining of Ebi3 was similar in CD4 T, CD8 T, and B cell subsets. A similar but non-identical pattern of IL12-p35 expression was seen when naïve B6 spleen cells were pulsed with T-reg derived exosomes (not shown). Lastly, we tested the CD4 T, CD8 T, and B cells for expression of exhaustion markers PD1, LAG3, and TIM3. Fig 4
shows images from population microscopy, depicting the appearance of IL35-xD cells. The punctate surface staining of Ebi3 was similar in CD4 T, CD8 T, and B cell subsets. A similar but non-identical pattern of IL12-p35 expression was seen when naïve B6 spleen cells were pulsed with T-reg derived exosomes (not shown). Lastly, we tested the CD4 T, CD8 T, and B cells for expression of exhaustion markers PD1, LAG3, and TIM3. Fig 4 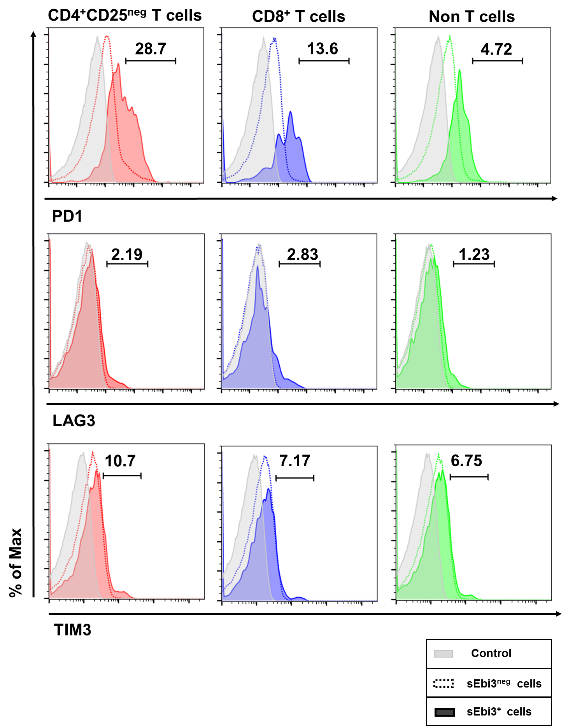 shows the results. Exhaustion was confined to the IL35-xD cells.
shows the results. Exhaustion was confined to the IL35-xD cells.
Conclusion: Tregs use various cytokines to suppress, but they greatly expand their influence with IL35-coated exosomes. These exosomes left a “mark”, punctate surface IL35 expression, while also promoting exhaustion. We are currently testing the "cell-bound cytokine" or CBC assay for xD-IL35 in clinical transplant recipients, as a means of monitoring their donor antigen-specific suppression, and progress toward T & B cell exhaustion.
