Establishment of Insulin-Producing Cells Differentiated from Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using a 3D-Culture System with Xeno-Antigen free Reagents
Mitsuo Shimada1, Rui Feng1, Tetsuya Ikemoto1, Yuji Morine1, Satoru Imura1, Shuichi Iwahashi1, Yu Saito1, Chie Takasu1.
1Department of Surgery, Tokushima University, Tokushima, Japan
Background: We have reported a new effective protocols to generate insulin-producing cells (IPCs) form adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) in rats using the new cell culture system with 3D scaffold named “compound X”* and xeno-antigen free reagents (ESOT 2017). The aim of this study is to clarify effectiveness of our 3D-culture system and xeno-antigen free reagents on differentiation of human ADSCs (hADSCs) to functional IPCs.
Methods: 2x104 commercial human ADSCs (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc, USA) plus 0.02mg of “compound X” per well were seed in 96-well U bottom plate, then our 2-step differentiation protocol for IPCs was applied using DMEM/F12 containing such as 1% human albumin instead of FBS and 1mM valproic acid. After the two-step differentiation finished (21 days), the cell morphology, dithizone (DTZ) and insulin staining, glucose stimulation test, were investigated. As a preliminary study, IPCs were transplanted under renal capsule in streptozotocin- induced diabetic nude mice.
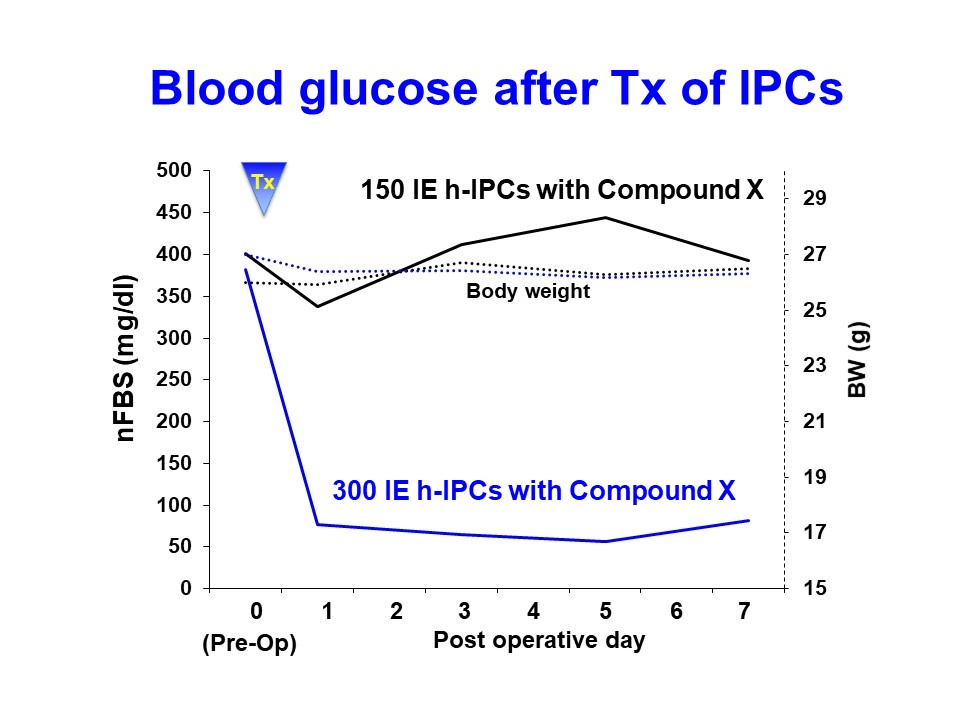
Results: In 24 hours after seeding ADSCs, the ADSCs began to form a cluster and keep the shape during differentiation. The average diameter of differentiated cell clusters is 830 μm. The differentiated cell clusters showed the positive DTZ and insulin staining. The insulin secretion of 10 differentiated cell clusters was 533 pmol/L per 60 minutes when exposed to 2.2 mM glucose, and it increased to 1,887 pmol/L when stimulated by 25mM glucose. The stimulation index of differentiated group (3.3) was significantly higher than that of undifferentiated group. High glucose level in diabetic mice using IPCs from 300 IE but not 150 IE from hADSCs dropped to normal range and maintained it level up to sacrifice (7days after transplantation) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Our new differentiation protocol from hADSCs to IPCs using our 3D-culture system and xeno-antigen free reagents is effective and promising for clinical transplantation targeted to Type-I DM patients.
* The name of this compound can not be disclosed due to the intellectual property right.