Transgenic Expression of hCD47 on Vessels in Porcine GalTKO Lung Grafts in Baboons may Mitigate Acute Vascular Rejection in Baboons: Up to 13 Days Graft Survival in Baboons
Hironosuke Watanabe1, Shunichiro Nomura1, Hisashi Sahara2, Thomas Pomposelli1, Yuichi Ariyoshi1, Lennan K Boyd1, Dilrukshi K Ekanayake-Alper1, Tatsu Tanabe1, Harrison C Glor1, Scott Arn1, Robert J Hawley1, Akira Shimizu2, David Ayares4, Marc I Lorber3, Megan Sykes1, David H Sachs 1, Kazuhiko Yamada1.
1CCTI/Surgery, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, United States; 2Department of Organ Replacement and Xenotransplantation Surgery, Kagoshima University, Kagoshima, Japan; 3Lung BioTechnology PBC, Silver Spring, MD, United States; 4Revivicor, Blacksburg, VA, United States
Background: Despite recent progress in survival times of xenografts in nonhuman primates, there are no reports of survival beyond 5 days of histologically well-aerated porcine lung grafts in baboons. Here we report our initial results of pig-to-baboon xeno lung transplantation (XLTx).
Methods: Study 1: Eleven baboons received genetically modified porcine left lungs as primary grafts that were histologically confirmed to be either GalT-KO alone (n=3), GalT-KO/humanCD47(hCD47)/hCD55 (n=3), GalT-KO/hD47/hCD46 (n=4) or GalTKO/hCD39/hCD55/hTBM/hEPCR (n=1) Tg swine. Study 2: Three porcine lung grafts were transplanted to baboons that had received a tolerance-inducing regimen and showed pig specific unresponsiveness in vitro by IFNg ELISPOT and FACS analysis. Two of these were hCD47+ GalTKO lungs and the third was GalTKO alone.
Results: Study 1: Survivals of primary lung grafts were 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 5, 6, 7, >7, 9 and 10 days. One baboon with graft survival >7 days, whose entire lung graft remained well-aerated, was euthanized on POD7 due to malfunction of femoral catheters. No statistical difference was seen in preformed nAb cytotoxicity levels between >7 day survivors and others (20% vs 27%). hCD47 expression of donor lungs was detected on both endothelial cells (ECs) and alveoli (Alv) only in the three grafts surviving >7, 9 and 10 days. All other grafts lacked hCD47 expression in endothelial cells and were completely rejected with diffuse hemorrhagic changes and antibody/complement deposition detected in association with early graft loss. Study 2: Delayed pig lung transplant survivals were 2 days (GaTKO alone), 4 days (hCD47+/GalTKO) and 13 days (hCD47+/GalTKO). The lung graft of the 13-day survivor expressed hCD47 on both ECs and Alv while the graft of the 4-day survivor expressed hCD47 only on Alv.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is first evidence of histologically viable porcine lung grafts up to 13 days in baboons. Our results indicate that GalT-KO pig lungs are highly susceptible to acute humoral rejection. Transgenic expression of hCD47 on vascular ECs in porcine GalTKO lung grafts appeared to be important to mitigate acute vascular rejection in baboons. 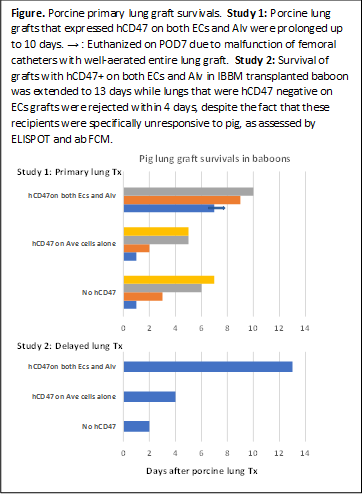
Lung Biotechnology PBC. NIH P01AI45897.
