Urinary TIMP-2 predicts the presence and duration of delayed graft function in DCD kidney transplant recipients
Jonna Bank1, Renee Ruhaak2, Darius Soonawala1, Fred Romijn2, Cees Kooten van1, Christa Cobbaert2, Hans Fijter de1.
1Nephrology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands; 2Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands
Introduction: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) are promising biomarkers in acute kidney injury. Here, we investigated the performance of both cell cycle arrest markers in predicting the occurrence and, in particular, duration of functionally defined delayed graft function (fDGF) in donation after circulatory death (DCD) kidney transplant recipients. Furthermore, it was investigated whether their predictability improved in case samples were corrected for dilution with osmolality.
Methods: Seventy-six consecutive DCD recipients were included. Immunosuppression consisted of anti-CD25 antibody induction and triple maintenance therapy (steroids, MMF and CNI). TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 were measured in urine by ELISA on post-operative day (POD) 1-10, week 6 and month 6. Linear-mixed model analysis and ROC analysis were performed.
Results: Fifty-one renal transplant recipients suffered from fDGF (67.1%), of which 14 patients had prolonged fDGF (≥21 days; 27.5%). In the first 10 days post transplantation, TIMP-2 (p<0.001) and IGFBP7 (p=0.001) levels were significantly higher in patients with compared to those without fDGF. On POD-1, TIMP-2 adequately identified patients with fDGF, with an AUC of 0.89, while IGFBP7 was only moderately accurate (AUC 0.63). On POD-10, TIMP-2 also predicted prolonged fDGF (AUC 0.77), whereas IGFBP7 did not. Correcting TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 values for dilution using osmolality slightly improved their predictability.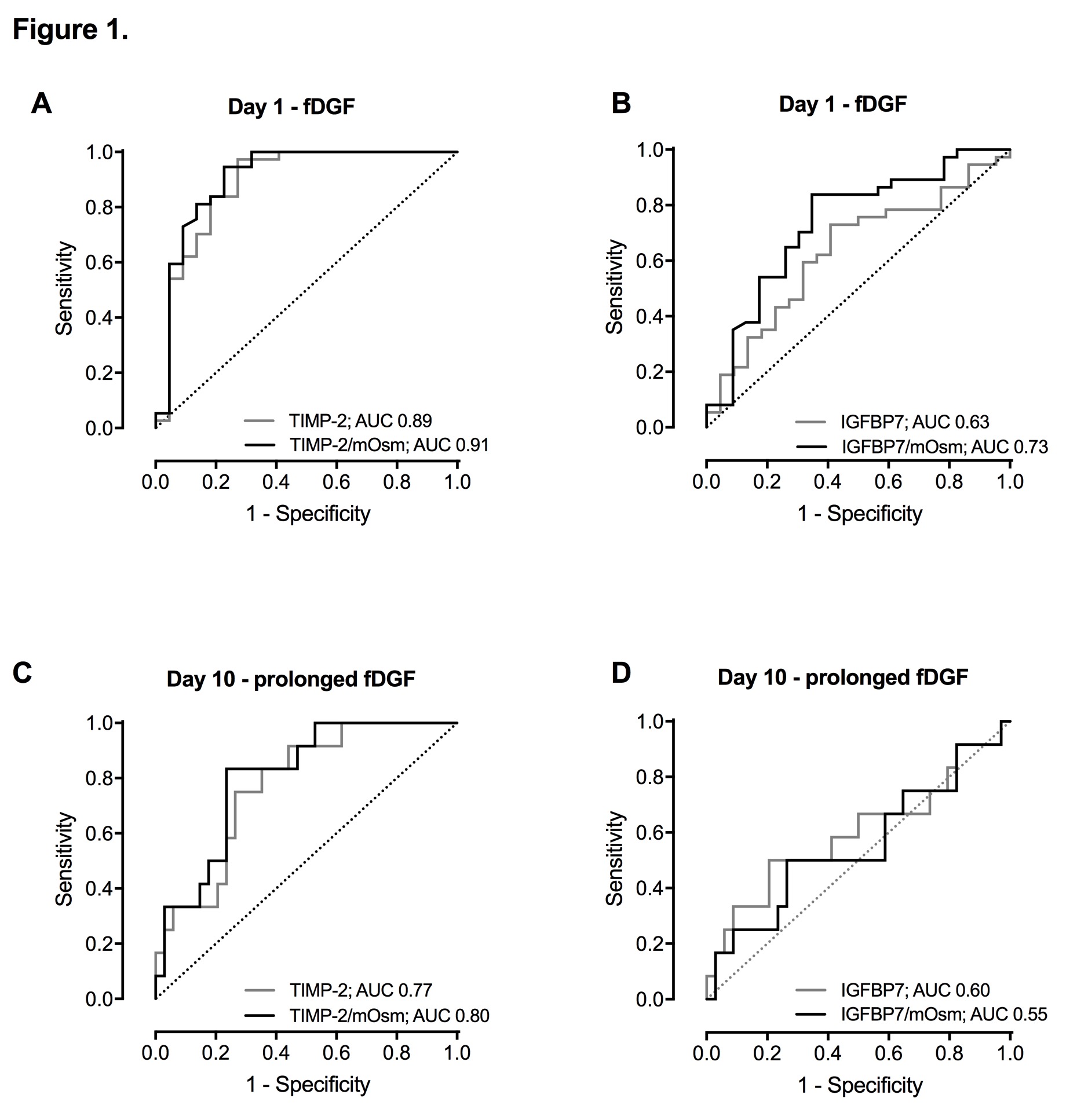 Multiplication of TIMP-2 with IGFBP7 was inferior as compared to TIMP-2 alone. Furthermore, with consecutive TIMP-2 values we were able to monitor the resolution of fDGF, with a decrease in TIMP-2 preceding the increase in eGFR.
Multiplication of TIMP-2 with IGFBP7 was inferior as compared to TIMP-2 alone. Furthermore, with consecutive TIMP-2 values we were able to monitor the resolution of fDGF, with a decrease in TIMP-2 preceding the increase in eGFR.
Conclusion: TIMP-2, but not IGFBP7, is a promising biomarker to predict the presence and duration of fDGF in DCD kidney transplant recipients.
