High Frequencies of CMV-specific CD8 and CD4 T Cell Subsets are Needed Pretransplant to Protect from CMV Replication in Kidney Transplant Recipients Treated with Thymoglobulin
María López-Oliva1, Virginia Martinez2, Aranzazu Rodriguez-Sanz2, Laura Álvarez1, María José Santana1, Rafael Selgas1, Carlos Jiménez1, Teresa Bellón2.
1Nephrology, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid, Spain; 2Institute of Health Research, Hospital Universitario La Paz - IdiPaz, Madrid, Spain
Background: Diagnostic of CMV-specific T cell immunity in solid organ transplant patients is showing to be a useful tool in predicting CMV infection after transplantation. Induction treatment with anti-lymphocyte polyclonal antibodies (thymoglobulin) causes lymphocyte depletion from the first week to beyond one-year post-trasplantation. Pretransplant immunological analysis in patients treated with thymoglobulin could guide the most appropriate prevention strategy.
Methods: We performed a prospective study of patients with kidney transplant who were treated with thymoglobulin as induction treatment and with universal prophylaxis for CMV infection. CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses to pp65 and IE-1 CMV antigens in 37 CMV-seropositive and 9 CMV-seronegative patients were investigated. Intracellular flow cytometry was employed to determine IFN-γ production as a functional readout. The response was analyzed in pretransplant samples and at 1, 6, 12 and 24 months post-transplant.
Results: In CMV-seropositive patients who did not develop CMV infection post-transplant, pretransplant CD8 T-cell response to IE-1 (p= .004) and CD8 and CD4 T-cell responses to pp65 (p=.04 and p=.002, respectively) were significantly higher than it in patients with CMV replication (Figure 1)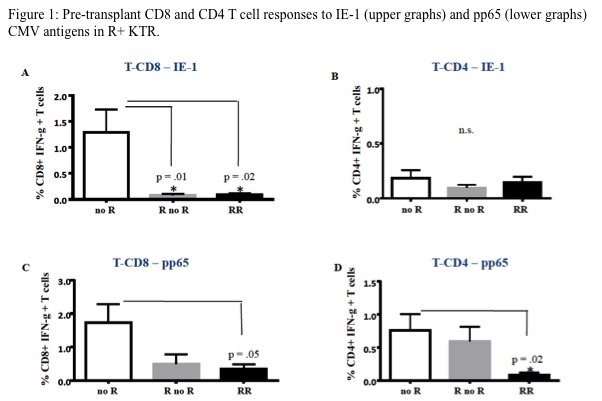 ROC curve analysis showed that low frequencies of IE-1-specific (< .13%) or pp65-specific (< .88%) CD8 T cells or pp65-specific (< .13%) CD4 T cells predicted the development of CMV infection (Figure 2)
ROC curve analysis showed that low frequencies of IE-1-specific (< .13%) or pp65-specific (< .88%) CD8 T cells or pp65-specific (< .13%) CD4 T cells predicted the development of CMV infection (Figure 2)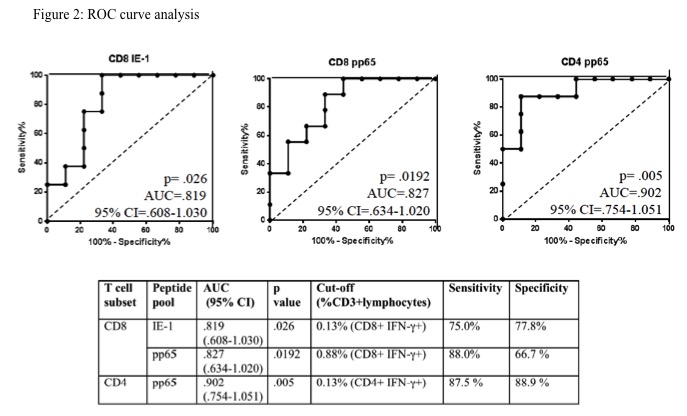
Conclusions: Functional assessment of pretransplant CMV-specific CD4 and CD8 T-cell immunity in seropositive patients who are going to receive thymoglobulin allows the identification of patients at risk of developing CMV infection post-transplantation.
