East vs West: Predictors of Oncologic Outcomes Following DD and LD Liver Transplantation for HCC
Varvara A Kirchner1, Gi-Won Song2, Steven Mongin1, Jae Hyun Kwon2, Sek Hwan Kim2, Eunyoung Tak2, Danielle Berglund1, Srinath Chinnakotla1, Raja Kandaswamy1, William Payne1, Timothy L Pruett1, Sung-Guy Lee2.
1Division of Transplantation, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States; 2Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery, Asan Medical Center and University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
AMIT - Asan and University of Minnesota Collaboration.
Background: Tumor recurrence is the most common cause of recipient death following liver transplantation(LT) for HCC. Outcomes following DD(deceased donor) vs. LD(living donor) LT for HCC have been variable. The aim of the current international collaboration is to elucidate predictors of the oncologic outcomes following DDLT and LDLT for HCC between two centers in Korea and US.
Methods: Between 2005-2015, 1175 LTs were performed for HCC(Korea:85/921; US:DD/LD:147/22). HCC recurrence, patient survival(PS) and recurrence-free survival(RFS) following DD and LDLT were compared between centers. Recipient and donor characteristics, median time from HCC diagnosis to LT, pre-LT HCC treatment, AFP, radiologic characteristics, and explant data were studied for recipients with and without HCC recurrence. Timing and inital recurrence site were analyzed.
Results: Recurrence rates were 17%/10% for DDLT and 14%/41% for LDLT(P<0.05), for Korean and US centers respectively. For Korea/US: 1-yr PS 85%/87%, 5-yr PS 70%/69% following DDLT. For Korea/US: 1-yr PS 94%/82%, 5-yr PS 82%/50% following LDLT(P<0.05)(Figure 1).For Korea/US, 5-yr RFS 86%/92% following DDLT, 83%/65% following LDLT (Figure 2)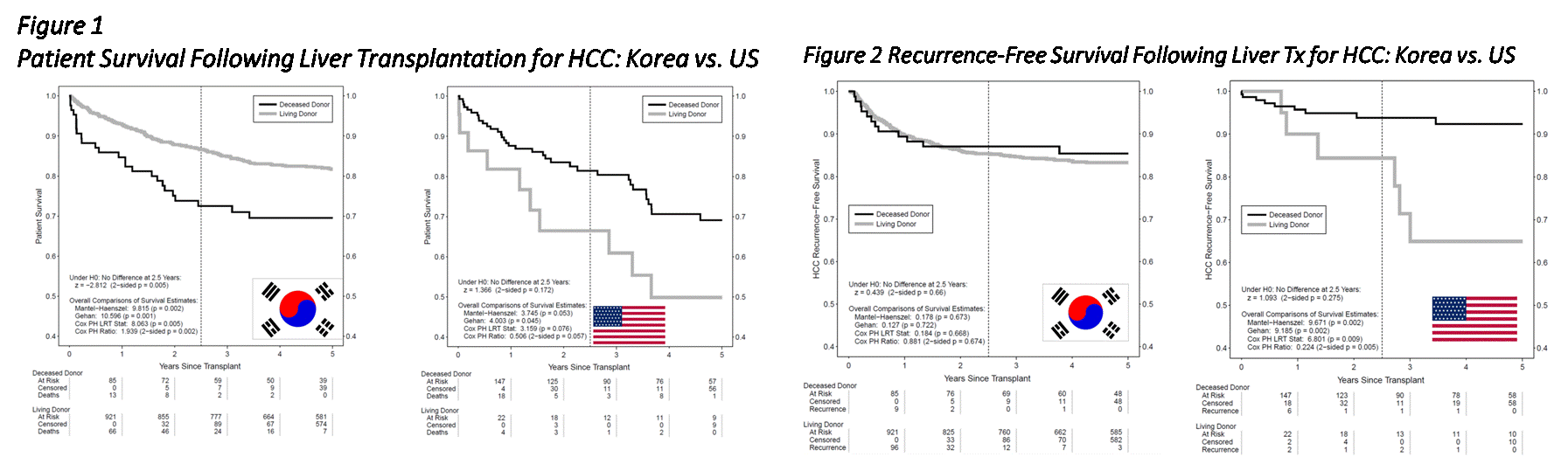 .HBV was prevalent cause of liver disease among Korean population(86%); HCV for US(79%)(p<0.05). Korean/US DD recipients had higher mean MELD(25/29) vs Korean/US LD recipients(13/18)(p<0.05). US recipients had shorter wait time from HCC dz to transplant(9/17 months for LD/DD) vs. Korean recipients(22/>25 months for LD/DD)(Table 1,2) (p<0.05)
.HBV was prevalent cause of liver disease among Korean population(86%); HCV for US(79%)(p<0.05). Korean/US DD recipients had higher mean MELD(25/29) vs Korean/US LD recipients(13/18)(p<0.05). US recipients had shorter wait time from HCC dz to transplant(9/17 months for LD/DD) vs. Korean recipients(22/>25 months for LD/DD)(Table 1,2) (p<0.05)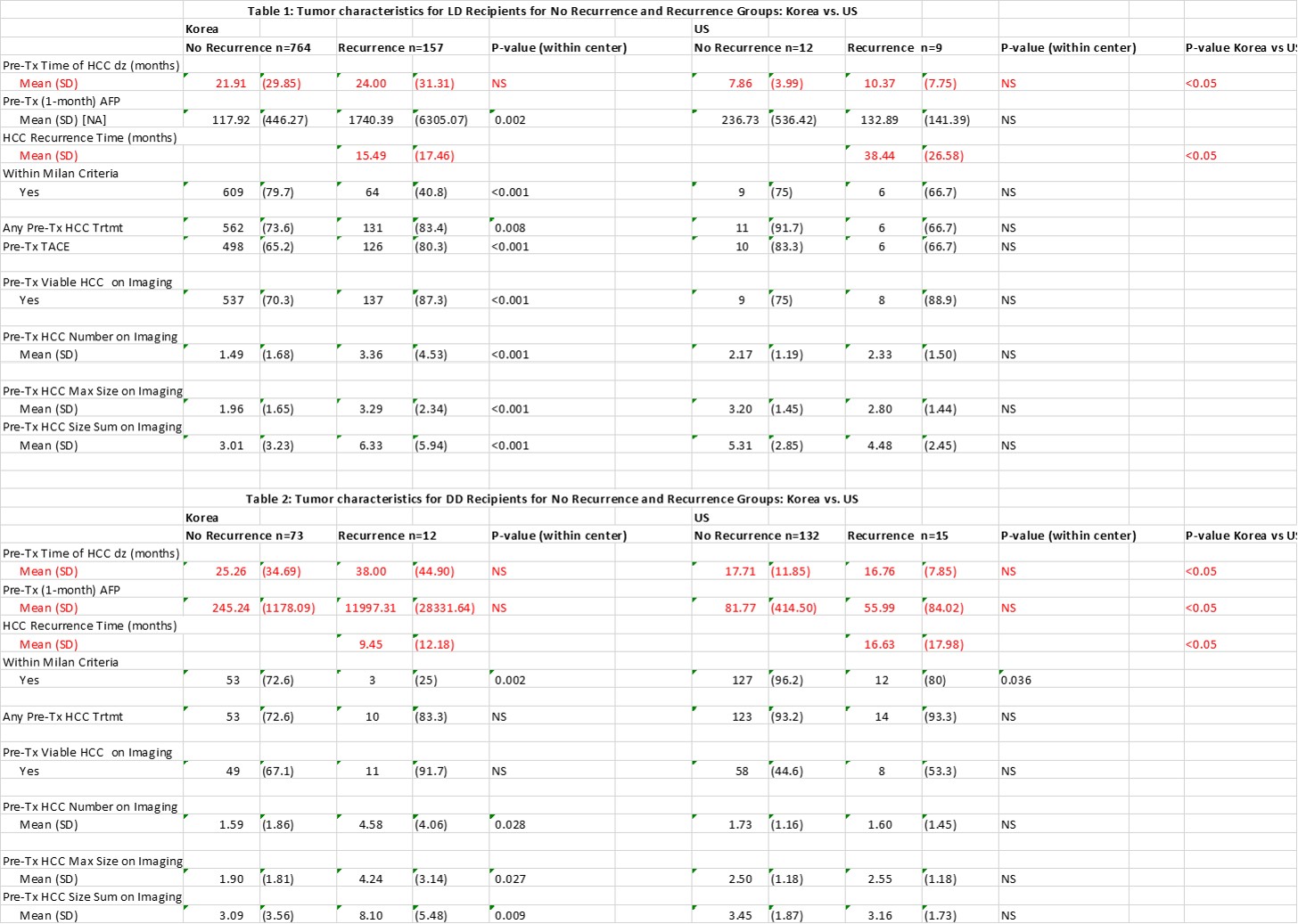 .Specific pre-tx tumor characteristics are reported, Tables 1&2. Among US recipients, tumor recurrence was later, but pattern of recurrence was similar between centers and donor types(graft 21%, extrahepatic 71%, graft/extrahepatic 8%). More aggressive explant pathology was associated with higher recurrence rate for LD/DD Korean and DD US recipients.
.Specific pre-tx tumor characteristics are reported, Tables 1&2. Among US recipients, tumor recurrence was later, but pattern of recurrence was similar between centers and donor types(graft 21%, extrahepatic 71%, graft/extrahepatic 8%). More aggressive explant pathology was associated with higher recurrence rate for LD/DD Korean and DD US recipients.
Conclusion: Better predictors of HCC recurrence in LDLT need to be delineated other than time from diagnosis to transplant. AFP, tumor size, and number didn’t provide sufficient discrimination. Better predictors would identify a population with low recurrence risk and allow early LDLT with improved outcomes.
