
Changes in Vitamin D levels After Kidney Transplantation
Korntip Phonphok1, Nakul Datta1, Joanna Schaenman1, Erik Lum1, Suphamai Bunnapradist1.
1Medicine-Nephrology, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Introduction: Low levels of serum vitamin D are common and associated with progression of chronic kidney disease. However, the frequency of hypovitaminosis D following kidney transplantation (KT) is not well studied. We examined how vitamin D levels change post-transplant and compared the changes between patients with low-and normal-vitamin D pre-transplant.
Materials and Methods: We examined KT recipients from January 1, 2006, to May 31, 2016, who had 25-hydroxy vitamin D tests both before and within the first year of KT. If there were multiple vitamin D levels, we took the closest value to the transplant date and defined as pre-Tx and post-Tx vitamin D levels. Patients with vitamin D levels greater than 50 were excluded. Patients were divided into two groups according to vitamin D levels, 1) low (<30) and 2) normal (30-50). Mean vitamin D levels were compared between pre-and post-Tx using t-test analysis.
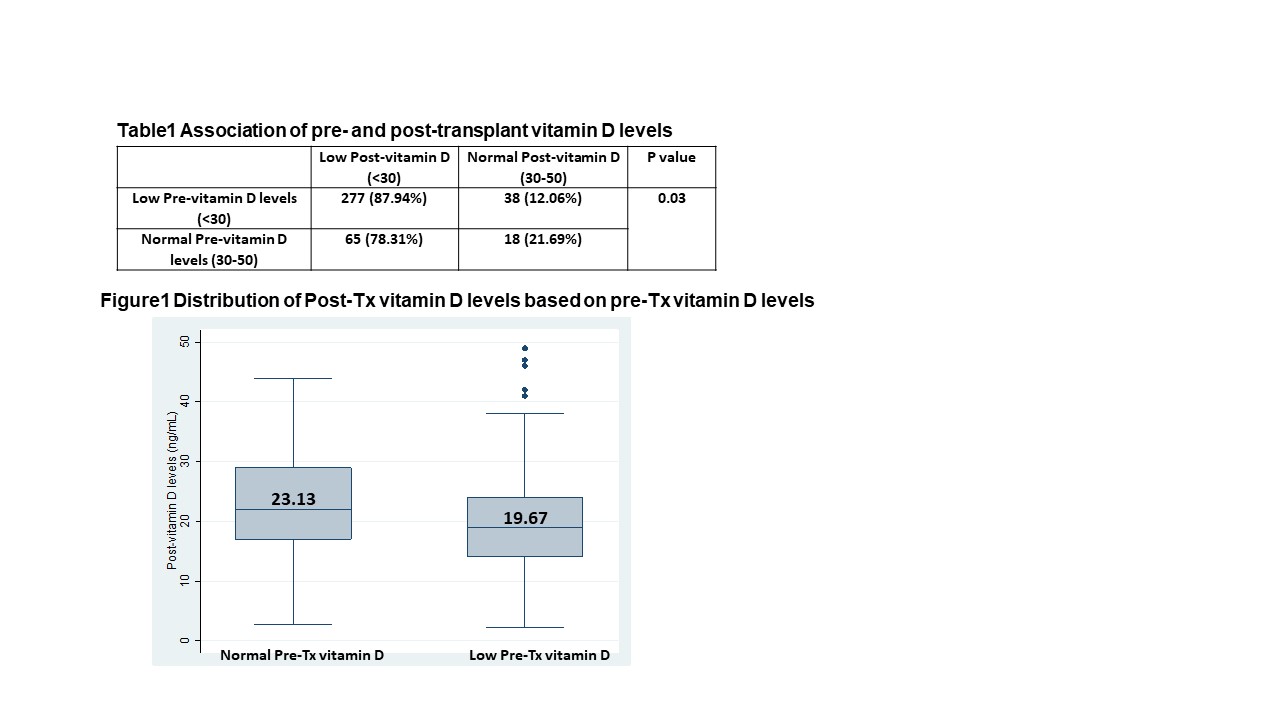
Results: A total of 398 patients were included in this study. Mean pre-and post-Tx vitamin D levels were 21.12 and 20.39 ng/mL, respectively. We found that 315 patients (79.15%) had low pre-Tx vitamin D levels and 83 patients (20.85%) had normal pre-Tx vitamin D levels. Post-Tx vitamin D levels were 23.13 and 19.67 ng/mL in normal and low pre-Tx vitamin D patients, respectively (p<0.01)(figure1). Patients with low pre-Tx vitamin D levels were more likely to have low post-Tx vitamin D levels (p=0.03)(table1). Furthermore, we found that 60.5% of patients with decreasing post-Tx vitamin D levels had low pre-Tx vitamin D levels while patients with normal pre-Tx vitamin D levels had a greater reduction in post-Tx vitamin D levels than patients with low pre-Tx vitamin D (figure2).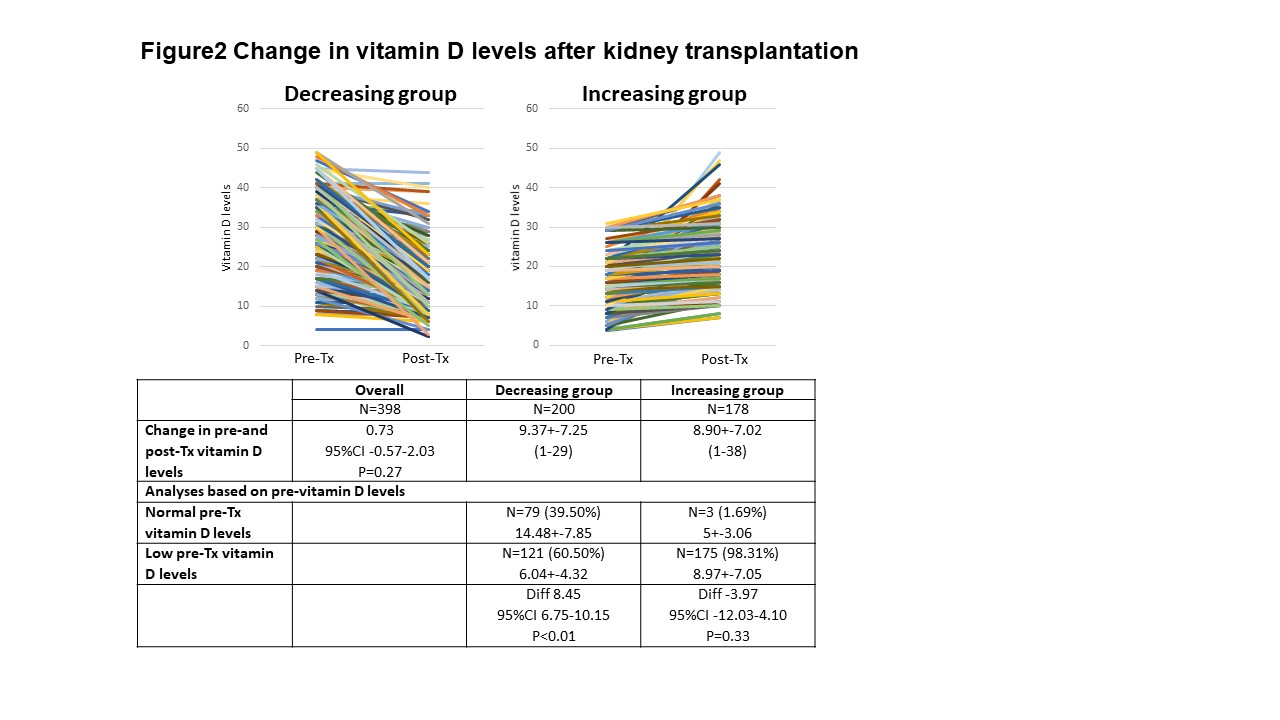
Conclusions: Hypovitaminosis D was very common in kidney transplant recipients. Preexisting hypovitaminosis D patients were more likely to have persistent low post-transplant vitamin D levels. Moreover, Post-transplant vitamin D levels were still lower than normal values regardless of pre-transplant vitamin D levels. Future studies should include vitamin D supplement and graft survival to support how vitamin D may impact on long-term outcome.
