Simultaneous Splenectomy is not Recommended in Living-Donor Liver Transplantation
Nobuhisa Akamatsu1, Rihito Nagata1, Yoshihiro Sakamoto1, Kiyoshi Hasegawa1.
1Artificial Organ and Transplantation Surgery Division, Department of Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Simultaneous splenectomy is preferentially performed in living-donor liver transplantation (LDLT) to modulate portal flow; increase postoperative platelet count, especially among those with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection; and immunomodulation in ABO-incompatible cases. The negative effects of the procedure, however, are not well established. Records of 395 LDLTs performed at our institution, including 169 patients (43%) with simultaneous splenectomy and 226 (57%) patients with spleen preservation, were reviewed with special reference to the simultaneous splenectomy cases. The most common indication for splenectomy was HCV-related disease (n=114), followed by low preoperative platelet count (n=52), and other reasons (n=3). Simultaneous splenctomy did not increase the platelet count in the early postoperative period (Figure 1).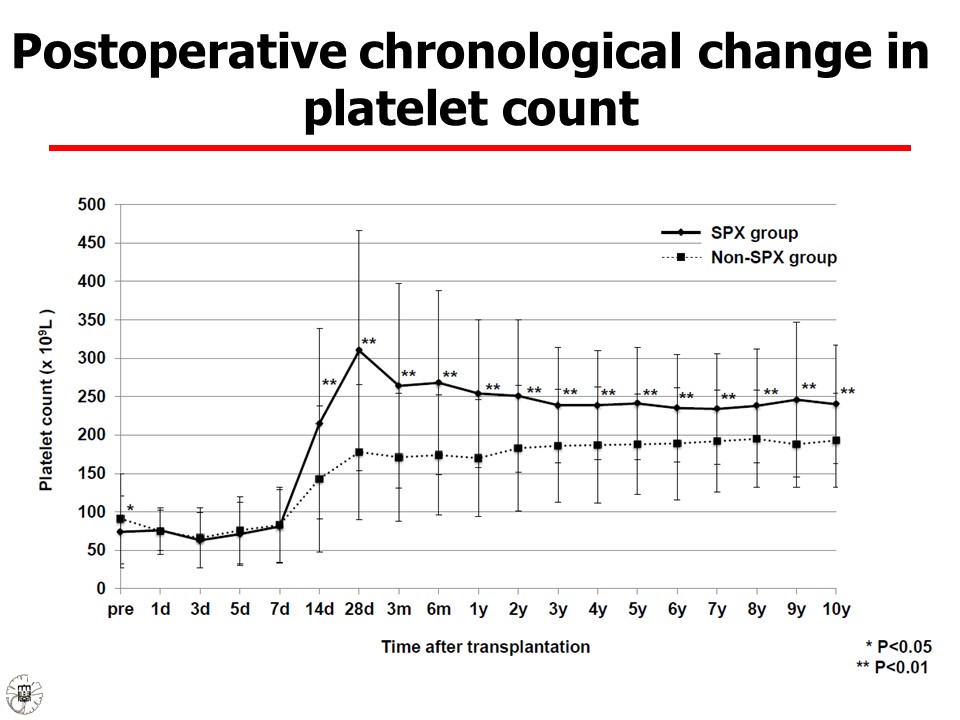 but the incidence of reoperation for postoperative hemorrhage was increased, mainly at the splenectomy site, within the first week. In addtion, the operative time, intraoperative blood loss, and incidence of lethal infectious disease were significantly higher in the splenectomy group, while the incidence of small-for-size syndrome was comparable between groups. Finally, splenectomy was an independent predictor for both postoperative hemorrhage (odds ratio [OR]=2.451, 95% confidence interval [CI]=1.285-4.815, P=0.006,(Table1)
but the incidence of reoperation for postoperative hemorrhage was increased, mainly at the splenectomy site, within the first week. In addtion, the operative time, intraoperative blood loss, and incidence of lethal infectious disease were significantly higher in the splenectomy group, while the incidence of small-for-size syndrome was comparable between groups. Finally, splenectomy was an independent predictor for both postoperative hemorrhage (odds ratio [OR]=2.451, 95% confidence interval [CI]=1.285-4.815, P=0.006,(Table1)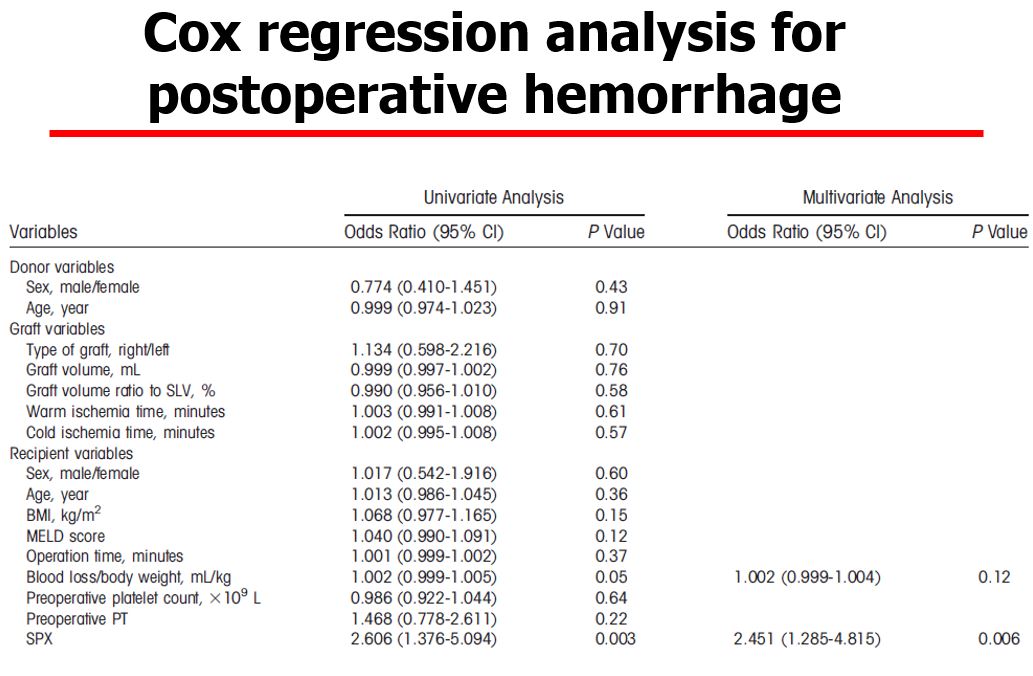 and lethal infectious complication (OR =3.748, 95% CI=1.148-14.001, P=0.03,Table 2.
and lethal infectious complication (OR =3.748, 95% CI=1.148-14.001, P=0.03,Table 2.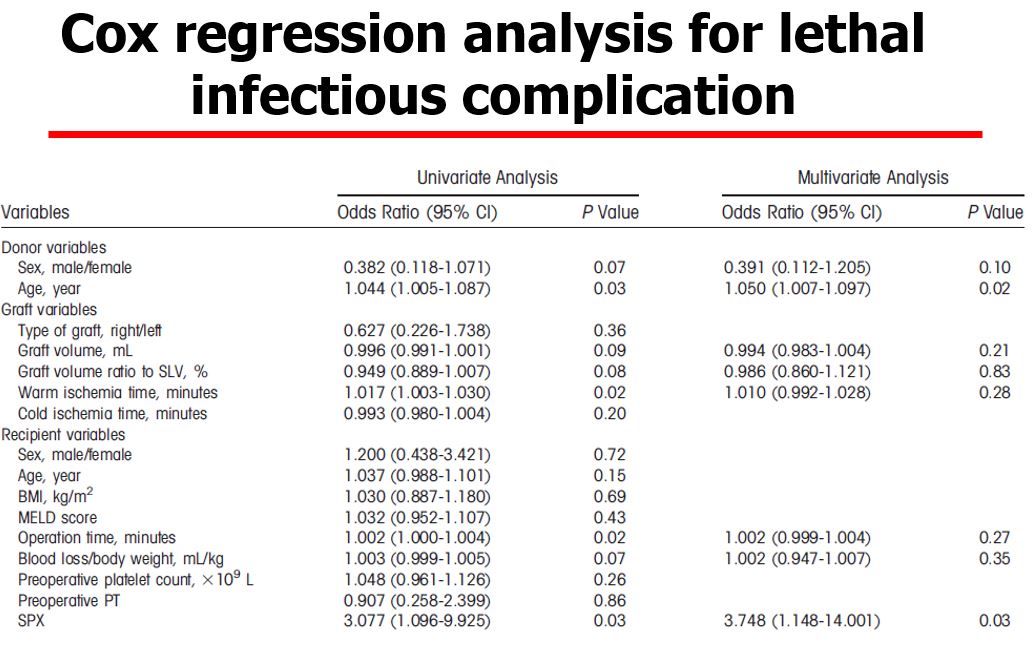 Based on the present findings, we do not recommend simultanenous splenectomy in LDLT.
Based on the present findings, we do not recommend simultanenous splenectomy in LDLT.
